Unlocking the future with explainable AI.
Abzu is the best in class in silico disease understanding and drug design company.
We accelerate the development of targeted, innovative drugs with our proprietary, explainable AI and in-house scientific expertise.
Abzu’s measurable impact in disease understanding and drug design.
Where proven results speak louder than promises, Abzu stands apart.
Dive into our curated collection of case studies, showcasing how Abzu’s cutting-edge technology is reshaping the landscape of disease understanding and drug design.
Abzu is your partner in understanding and design.
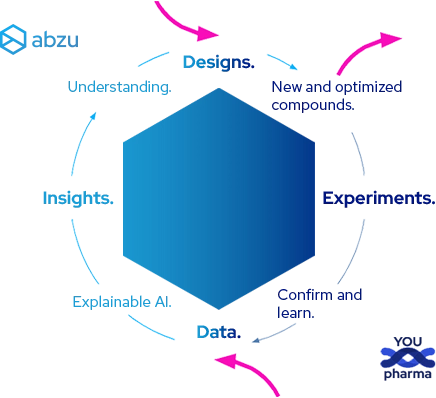
A cycle of innovation and optimization — to realization.
Whether we start with designs or your data, Abzu provides you the insights and confidence to accelerate your R&D and transform concepts into market-ready drugs.
Abzu’s story and mission:
Ready to transcend black-box AI and ordinary analytics?
Founded in 2018, Abzu has established itself as the best in class in silico disease understanding and drug design company.
Our proprietary explainable AI is the cornerstone of our approach. Combined with our in-house scientific expertise, we accelerate the development of new, innovative drugs.
“Abzu” is an Ancient Sumerian word meaning “subterranean water,” with an additional religious context of “the source of everything.”
The latest in cutting-edge research, perspective, and events.
Your next insight into understanding a disease or designing a new drug starts here.
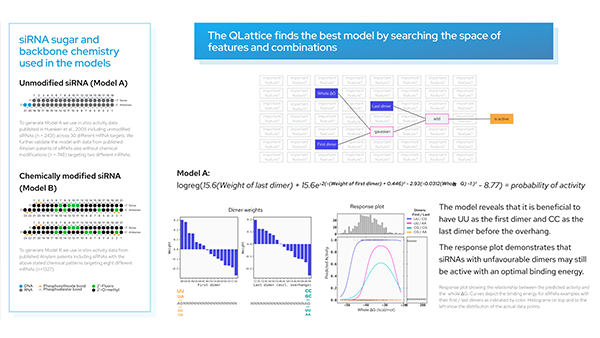
Here we use the QLattice® to generate siRNA activity models from publicly available data to create insights that can be used to design active siRNAs.
RNA Leaders Europe is the #1 event focused on the development of mRNA, RNAi, ASOs, oligonucleotides, vaccines, microRNAs, genome editing, wider nucleic acids & RNA targets.
The QLattice: Abzu’s proprietary explainable AI.
Experience the future of AI, where accuracy meets simplicity and explainability.
Models developed by the QLattice have unparalleled accuracy, even with very little data, and are uniquely simple to understand.
Research and insights powered by Abzu’s technology.
From our in silico lab to the frontiers of science.
We proudly showcase the extensive range of research journals where our technology has been cited. Each is a testament to how our proprietary explainable AI reveals groundbreaking insights in science.
Abzu is internationally recognized for our explainable AI.
We have an unwavering commitment to performance and ethical standards in AI and data use.
Disclaimer.
Gartner® and Cool Vendors™ are registered trademarks and service marks, and the Gartner Cool Vendor badge is a trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates, and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved. Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in our research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
Read the 2022 Gartner® Cool Vendors™ in AI Governance and Responsible AI — From Principles to Practice report.